GRINDING/MILLING/PARTICLE SIZE REDUCTION TECHNOLOGY & PRODUCTS
Pre-Breaker
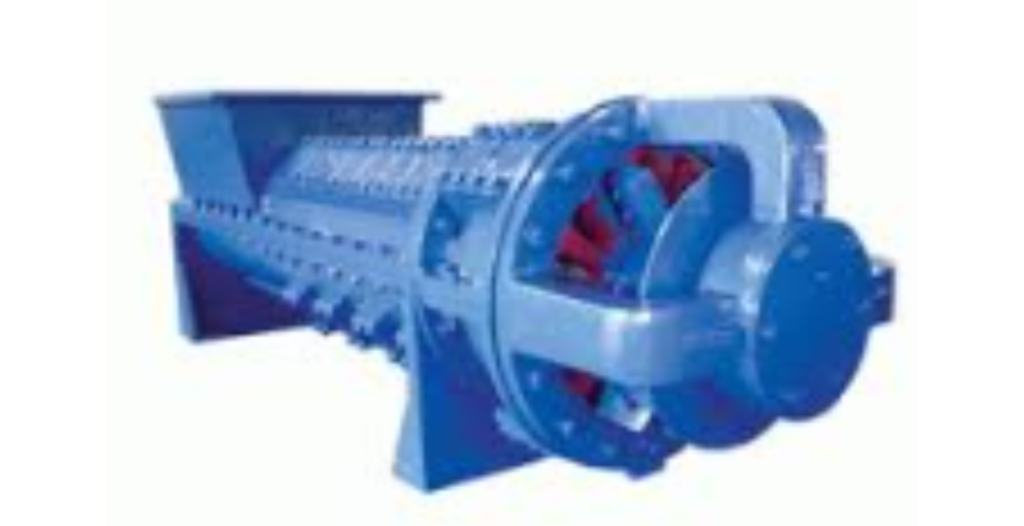
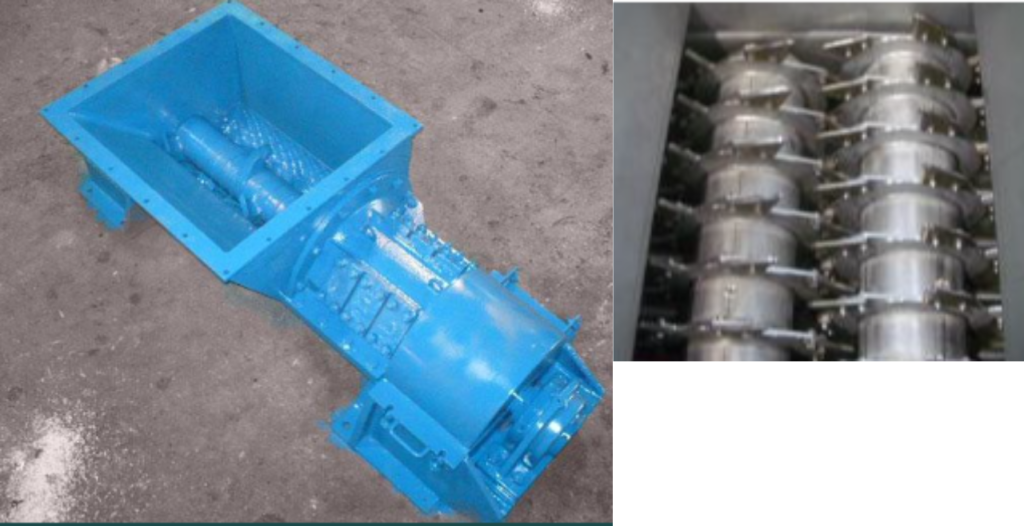
A Pre-Breaker, also known as a Pre-Breaker Mill, is a heavy-duty machine used in various industries for the initial coarse size reduction of large, bulky materials before further processing. These machines are designed to handle oversized items that are too large or irregularly shaped for downstream equipment. Below is a detailed overview of Pre-Breakers, including their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, applications, materials of construction (MOC), and a summary: |
| Working Principles: |
| The working principle of a Pre-Breaker involves the following steps: |
| Feeding: The material is loaded into the Pre-Breaker through a hopper or other feeding mechanism. |
| Crushing Action: Inside the machine, a heavy-duty rotor equipped with large blades or hammers rotates at a relatively low speed compared to some other size reduction equipment. The rotor’s slow speed generates high impact and shear forces on the incoming material. |
| Size Reduction: As the material passes through the Pre-Breaker, the blades or hammers impact, crush, and break down the oversized items into smaller, more manageable pieces. |
| Discharge: The reduced material is discharged from the Pre-Breaker, often onto a conveyor belt or into a container, where it can be further processed or transported. |

| Advantages: |
| Size Reduction: Pre-Breakers effectively reduce the size of large and bulky materials, making them suitable for downstream processes. |
| Improves Efficiency: Processing equipment downstream of the Pre-Breaker can work more efficiently with smaller, more uniform material. |
| Waste Reduction: In waste management applications, Pre-Breakers can compact and reduce the size of bulky waste materials, reducing the number of waste pickups required. |
| Enhanced Safety: By reducing the size of large items, Pre-Breakers help mitigate safety risks associated with handling oversized objects. |
| Disadvantages: |
| Initial Investment: Pre-Breakers can be expensive to purchase and install, particularly for heavy-duty or specialized models. |
| Maintenance: The heavy-duty nature of Pre-Breakers can result in high maintenance requirements, including blade or hammer replacement. |
| Energy Consumption: Pre-Breakers can consume a significant amount of energy, especially when processing very tough or hard materials. |
| Noise and Vibration: The operation of Pre-Breakers can generate noise and vibration, which may require noise control measures in some settings. |
| Applications: |
| Pre-Breakers find applications in various industries, including: |
| Waste Management: For compacting and reducing the size of bulky waste materials before disposal. |
| Manufacturing: For breaking down oversized or irregularly shaped materials in manufacturing processes. |
| Mining and Quarrying: To reduce large rocks and ore before feeding them into crushers or other processing equipment. |
| Construction and Demolition: For processing construction debris and large chunks of concrete or asphalt. |
| Heavy Industries: In industries where large or heavy materials need size reduction before further processing. |
| Materials of Construction (MOC): |
| The choice of materials for Pre-Breakers depends on the specific application and the materials being processed. Common materials of construction include: |
| Stainless Steel: Often used for the main structure and crushing components due to its corrosion resistance and suitability for food and pharmaceutical applications. |
| Carbon Steel: Suitable for many industrial applications but may require surface treatment for corrosion resistance. |
| Hardened Alloys: In applications where abrasion resistance is critical, hardened steel alloys may be used for the blades or hammers. |
| Summary: |
| A Pre-Breaker is a heavy-duty machine used to reduce large and bulky materials into smaller, more manageable pieces. It operates by crushing and breaking down oversized items, making them easier to handle, improving downstream process efficiency, and reducing safety risks associated with handling large objects. While Pre-Breakers offer advantages like size reduction and waste reduction, they also come with considerations like initial investment, maintenance, energy consumption, and noise and vibration generation. Materials of construction are selected based on the specific application’s requirements. |


 Sales & Marketing:
Sales & Marketing:  Service Supports:
Service Supports:  Website:
Website: 