mixers/blenders technology/products
diffusion blenders:
Diffusion blenders, also known as diffusion mixers, are a type of mixing equipment used in blending technology to combine dry powders, granules, and other solid materials.
They are designed to achieve thorough and consistent blending by promoting the diffusion of particles throughout the mixture.
Here’s an overview of their working principles, advantages, and disadvantages:

| Working Principle: Diffusion blenders work on the principle of promoting the random movement and interaction of particles to achieve blending. The key working principles include: |
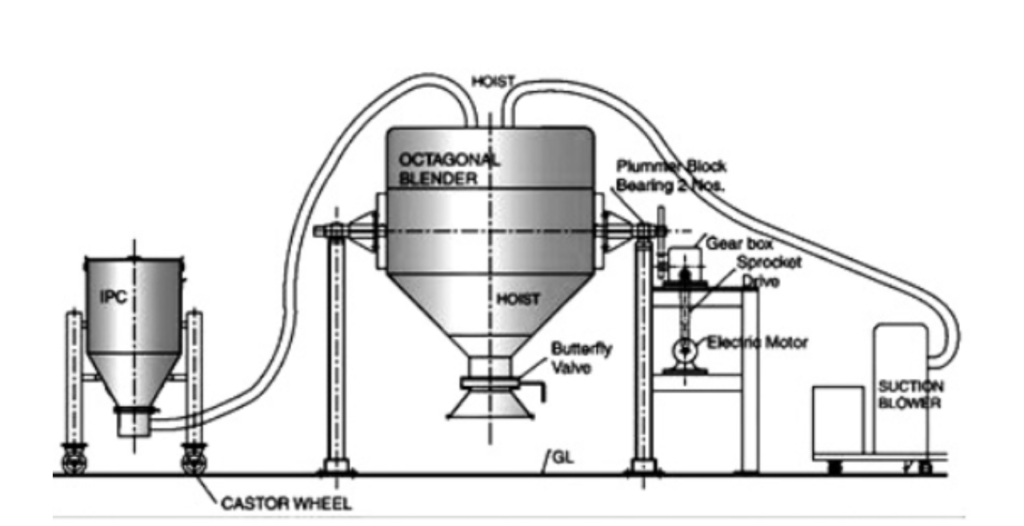
| Loading: The dry materials to be blended are loaded into the blender through an opening at the top. |
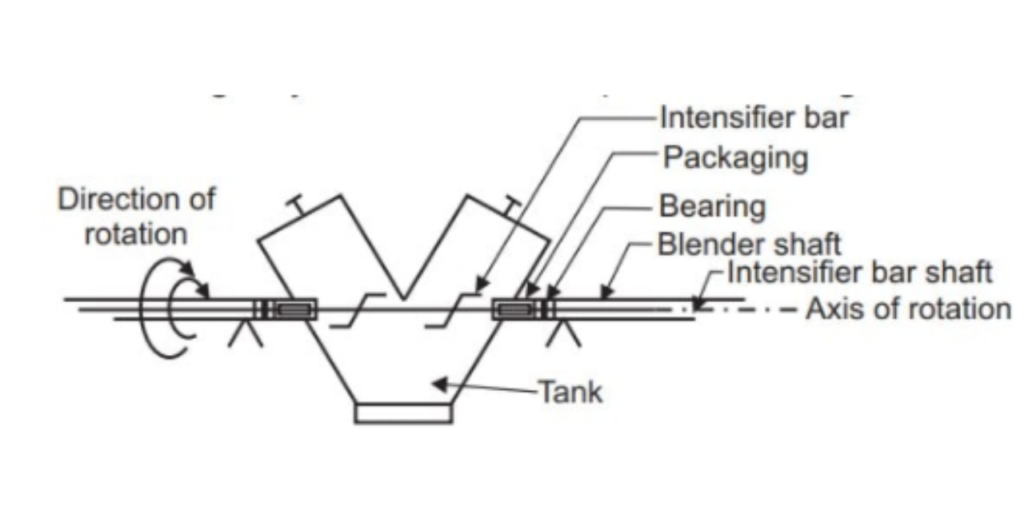
| Blending: Inside the blender, there are various mechanisms or components that facilitate the movement and diffusion of particles. These mechanisms can include rotating blades, agitators, or other internal elements. |
| Mixing: As the blender operates, the particles are subjected to mechanical forces that encourage random movement, collision, and diffusion. This mixing action ensures that the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. |
| Discharging: Once the blending process is complete, the blended mixture can be discharged through an outlet at the bottom of the blender. |

| Advantages of Diffusion Blenders: |
| Uniform Mixing: Diffusion blenders offer excellent mixing uniformity, ensuring that all components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. |
| Gentle Mixing: The mixing action is typically gentle on sensitive or fragile materials, reducing the risk of product degradation. |
| Versatility: They can handle a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, and materials with varying particle sizes. |
| Customization: The design and configuration of internal components can be tailored to meet specific blending requirements, making them suitable for various applications. |
| Ease of Cleaning: Many diffusion blenders are designed for easy cleaning and sanitation, which is essential for industries with strict hygiene requirements. |
| Disadvantages of Diffusion Blenders: |
| Limited for Cohesive Materials: Diffusion blenders may not be the best choice for highly cohesive or sticky materials that can agglomerate and hinder mixing. |
| Batch Process: They are typically used for batch processing, which may not be ideal for continuous production lines. |
| Complex Design: The design of diffusion blenders can be more complex, with various internal components, which may require more maintenance over time. |
| Material Flow Issues: Some materials may not flow well within the blender, leading to uneven mixing or material buildup. |
| Energy Consumption: Achieving thorough blending through diffusion can require significant energy input, especially for materials that are less prone to movement and diffusion. |

In summary, diffusion blenders are used for achieving uniform blending in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food processing, and more.
They rely on the promotion of random particle movement and diffusion to achieve mixing. While they offer excellent blending uniformity and are versatile, they may not be the best choice for highly cohesive materials or continuous production processes.
The choice of blender type should be based on the specific characteristics of the materials and the blending requirements of the process.


 Sales & Marketing:
Sales & Marketing:  Service Supports:
Service Supports:  Website:
Website: 